+ On TCP/IP connected: 15.19mV ~ 75.95mA
+ On downloading: 23.27mV ~ 116.35mA
+ On boot, wifi not connected: 15.64mV ~ 78.2mA
+ On deep sleep: 0.014mV ~ 0.7 (incorrect, its too small)
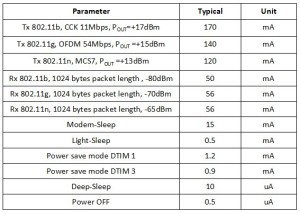
urrently ESP8266 can support three low power modes: Light Sleep, Modem Sleep and Deep Sleep.
①:Modem-Sleep requires the CPU to be working, as in PWM or I2S applications. According to 802.11 standards (like U-APSD), it saves power to shut down the Wi-Fi Modem circuit while maintaining a Wi-Fi connection with no data transmission.
E.g. in DTIM3, to maintain a sleep 300ms-wake 3ms cycle to receive AP’s Beacon packages, the current is about 15mA.
②:During Light-Sleep, the CPU may be suspended in applications like Wi-Fi switch. Without data transmission, the Wi-Fi Modem circuit can be turned off and CPU suspended to save power according to the 802.11 standard (U-APSD).
E.g. in DTIM3, to maintain a sleep 300ms-wake 3ms cycle to receive AP’s Beacon packages, the current is about 0.9mA.
③:Deep-Sleep does not require Wi-Fi connection to be maintained. For application with long time lags between data transmission, e.g. a temperature sensor that checks the temperature every 100s.
E.g. sleep 300s and waking up to connect to the AP (taking about 0.3~1s), the overall average current is less than 1mA.